May 13, 2025
Fiscal Year Ended March 31, 2025 (FY2024) Result Briefing (Sixth Mid-Term Management Plan Update Briefing)
- Briefing Video
-
 Briefing Material
(7,185KB)
Briefing Material
(7,185KB)
-
 Briefing Material w/ Script
(5,097KB)
Briefing Material w/ Script
(5,097KB)
-
 Q&A Summary
(214KB)
Q&A Summary
(214KB)
July 9, 2024
Sixth Mid-Term Management Plan Update Briefing
-
 Briefing Material
(4,253KB)
Briefing Material
(4,253KB)
-
 Briefing Material w/ Script
(2,432KB)
Briefing Material w/ Script
(2,432KB)
-
 Q&A Summary
(215KB)
Q&A Summary
(215KB)
April 6, 2023
Briefing of Vision 2035
(Long-Term Vision and Sixth Mid-Term Management Plan)
- Briefing Video
-
 Briefing Material
(11,246KB)
Briefing Material
(11,246KB)
-
 Briefing Material w/ Script
(5,194KB)
Briefing Material w/ Script
(5,194KB)
-
 Q&A Summary
(271KB)
Q&A Summary
(271KB)
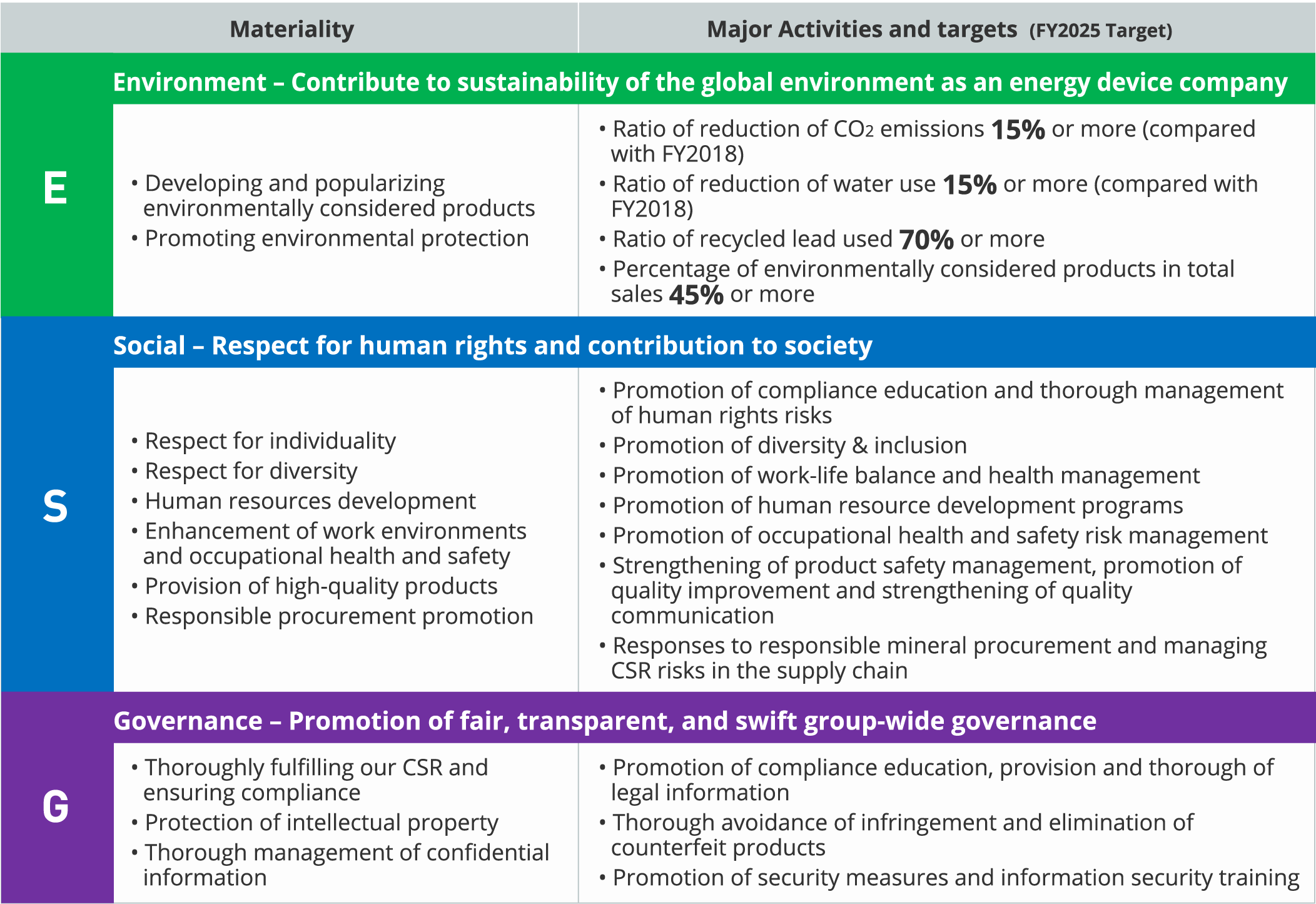
Based on the “Four Re’s” formula, we strive for innovation in energy technology, endeavor to address the challenges facing society through the development of mobility and other public infrastructures, and seek to create comfortable living environments and play our part in the global effort toward sustainability.
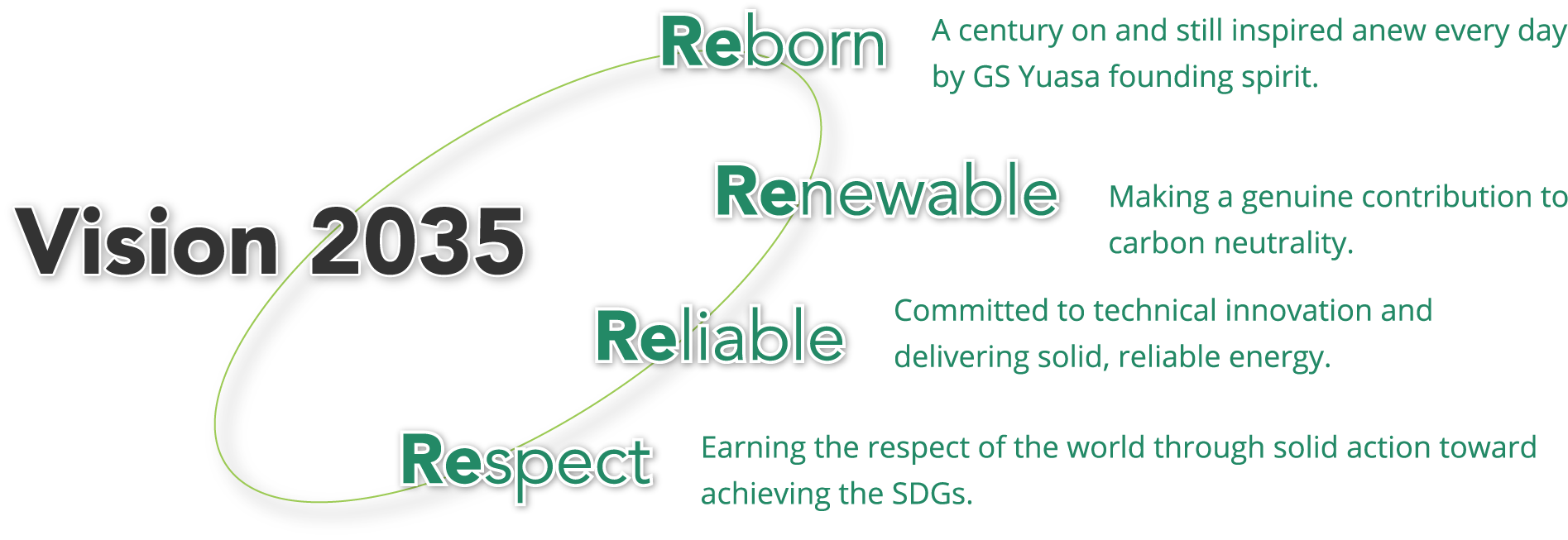
In order to contribute to the realization of a sustainable society, it is important for us to further innovate the technologies we have developed for storing and using electricity and to widely implement and operate these technologies in public infrastructure in order to solve social issues. In order to realize a sustainable society and to realize sustainable growth of our company, we have reviewed the "Management Vision and Management Policies" that we had previously established, and have now formulated a new "Policy on Sustainability Management Policy".
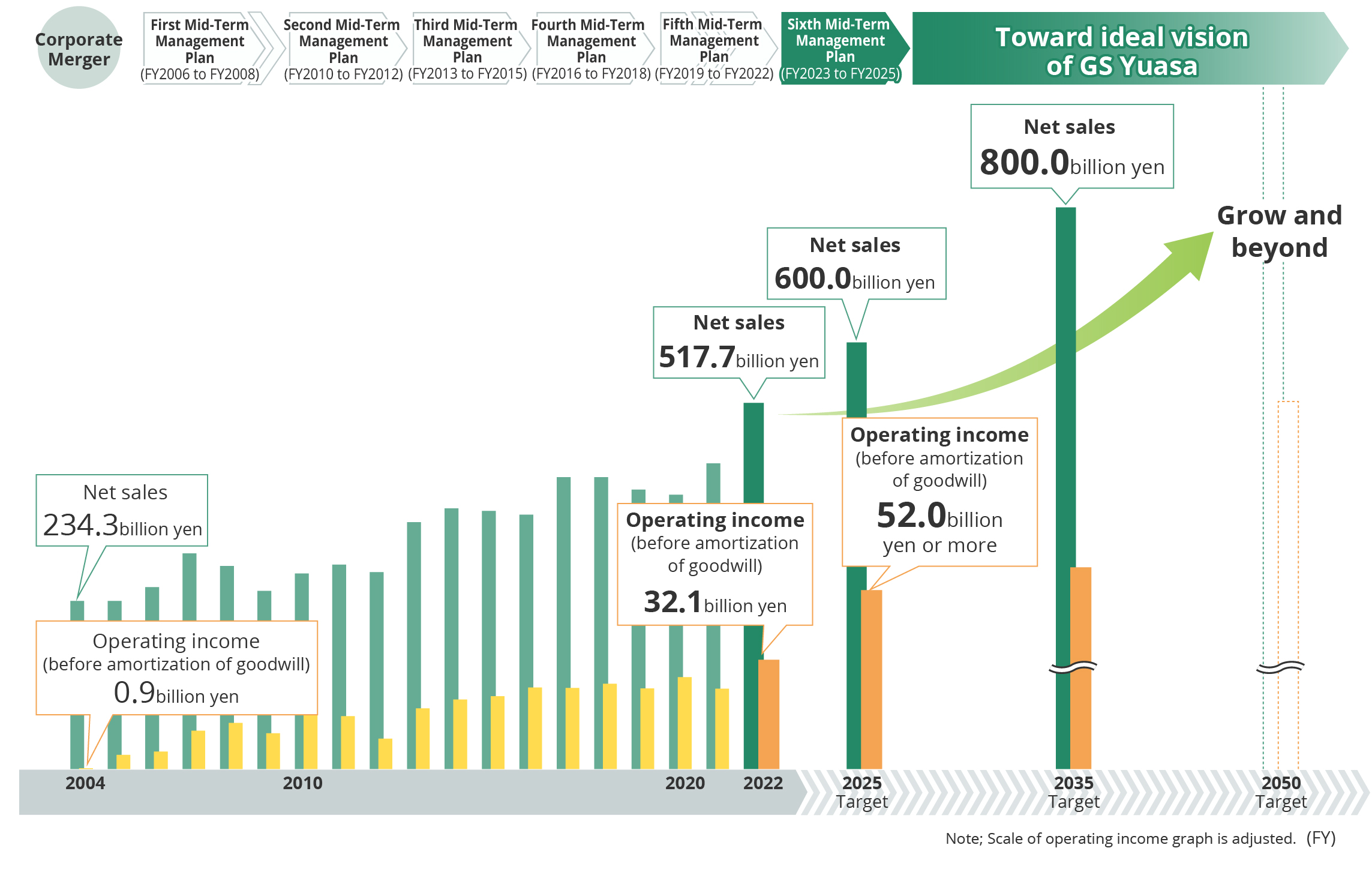
Vision 2035, which we have announced this time, shows "Vision of GS Yuasa in 2035" in order to achieve "Innovation and Growth" for the next 100 years, based on the DNA of our founders and the knowledge we have accumulated over the past 100 years.
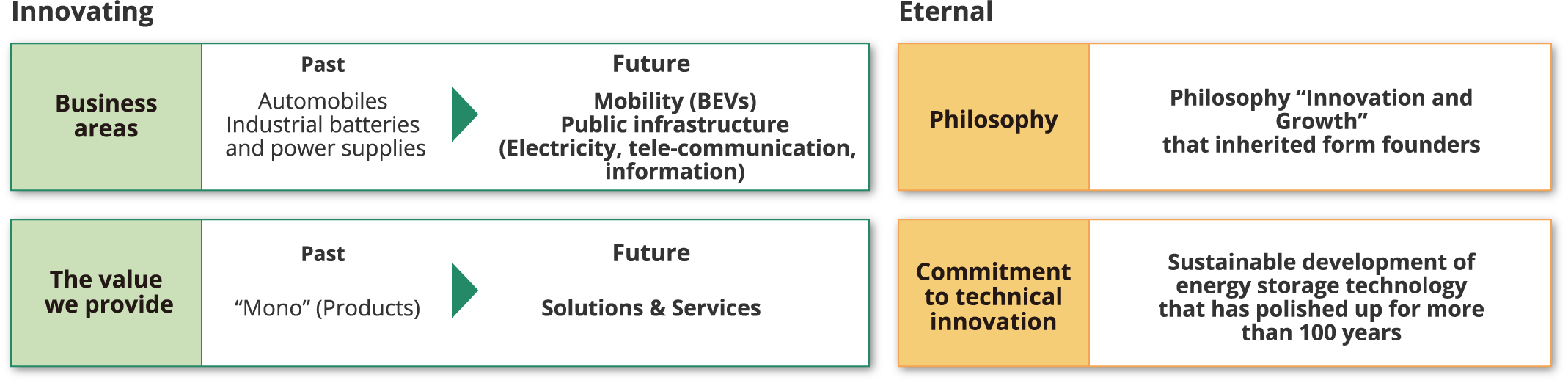
Achieving Vision 2035 requires two elements, some innovating and some eternal. In terms of elements that should not be changed are our philosophy and a commitment to technical innovation. Our philosophy “Innovation and Growth” inherited from the Company’s founders should not be changed as well as a commitment to technical innovation, namely the sustainable development of energy storage technology that has been polished up for more than 100 years. Conversely, we seek to innovate in business areas and in the value we provide. In the past, we have offered “mono,” that is “products” to customers, in the form of lead-acid batteries, lithium-ion batteries, power supply systems, etc. Going forward, in addition to products, we also want to offer solutions and services in the domains of mobility and public infrastructure, and aim to become a comprehensive device company.
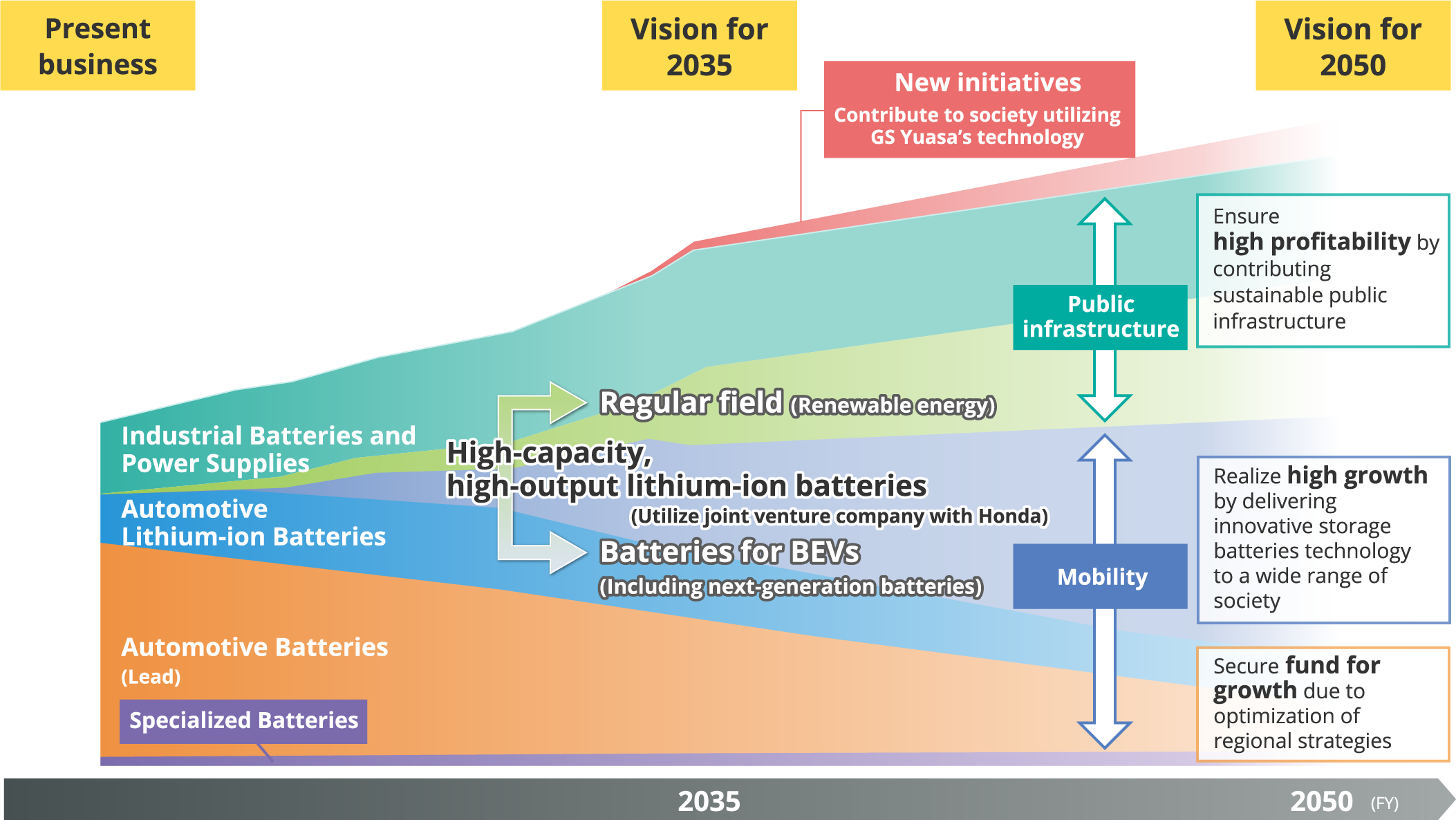
Here is a diagram showing the innovation and growth of our business toward achieving Vision 2035. Automotive Battery segment will be further improving profit margins, securing profits which we intend to use as investment capital for the growth domains of mobility and public infrastructure. Regarding the Automotive Lithium-ion battery segment, sales of lithium-ion batteries for HEVs are expected to increase through to around 2035, after which they will see a gradual decline. We believe there is and will continue to be strong demand in the Industrial Battery and Power Supply segment, centered around backup batteries and power supplies, as these play a role in the maintenance of public infrastructure. Toward 2035 and 2050, we will develop high-capacity, high-output lithium-ion batteries by utilizing our joint venture with Honda Motor Co., Ltd. and apply to batteries for BEVs and the regular field, centered around batteries for ESS. In terms of new initiatives, starting around 2035, we would like to nurture a new business contributing to society, and utilizing GS Yuasa’s technology and expertise acquired over the years.
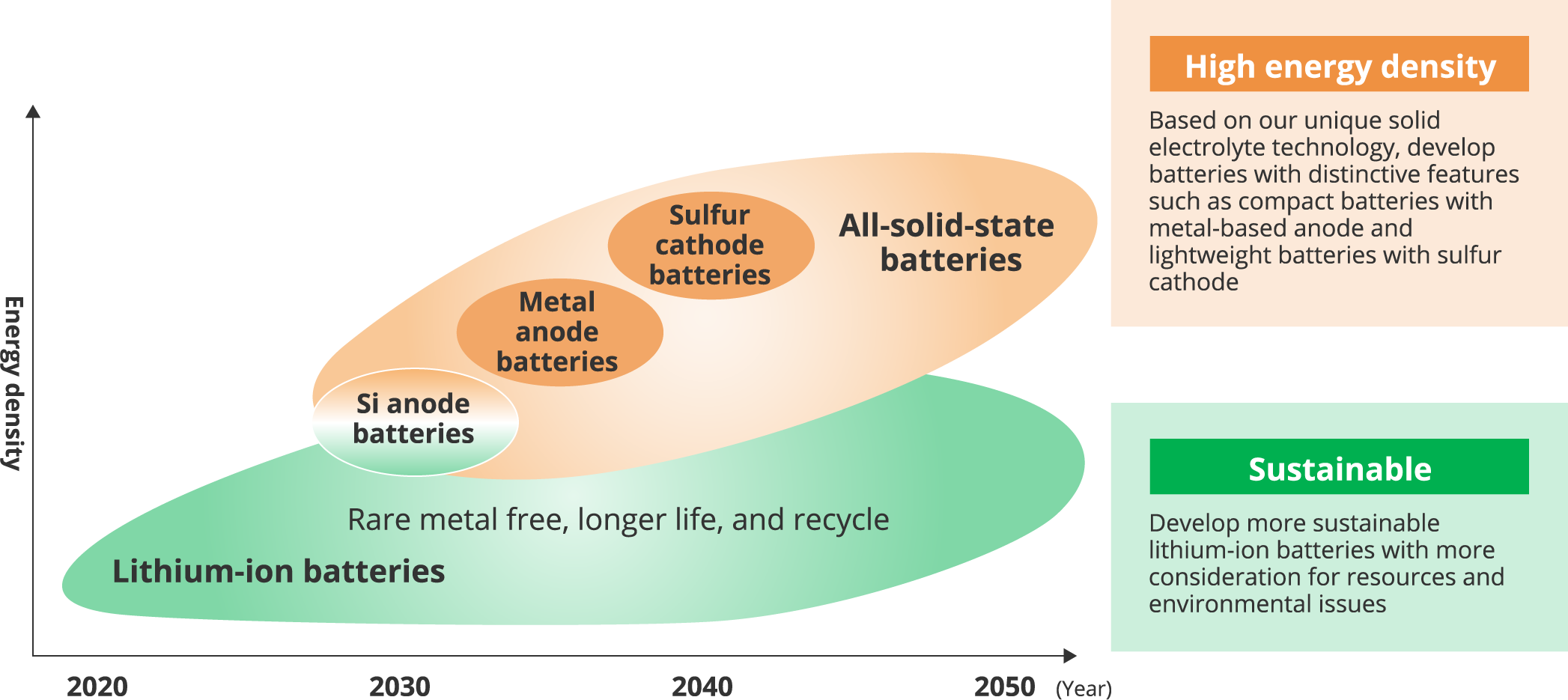
Liquid electrolyte lithium-ion batteries as they currently exist will evolve into batteries free from the use of rare metals, possessing longer lives, and capable of being recycled. As such, we will continue to develop more sustainable batteries with more consideration for resources and environmental issues. Regarding all-solid-state batteries, we are aiming to achieve higher energy density, and will be developing batteries with distinctive features, based on our unique solid electrolyte technology. We will be carrying out the development of silicon-based anodes, as opposed to carbon-based anodes as they currently exist, and furthermore, through the development of metal anode batteries, we will aim to achieve higher energy densities. In terms of cathode technology, sulfur presents several advantages, such as allowing for high-performance batteries. Reserves of this resource are also plentiful, and it’s also a low-cost material.
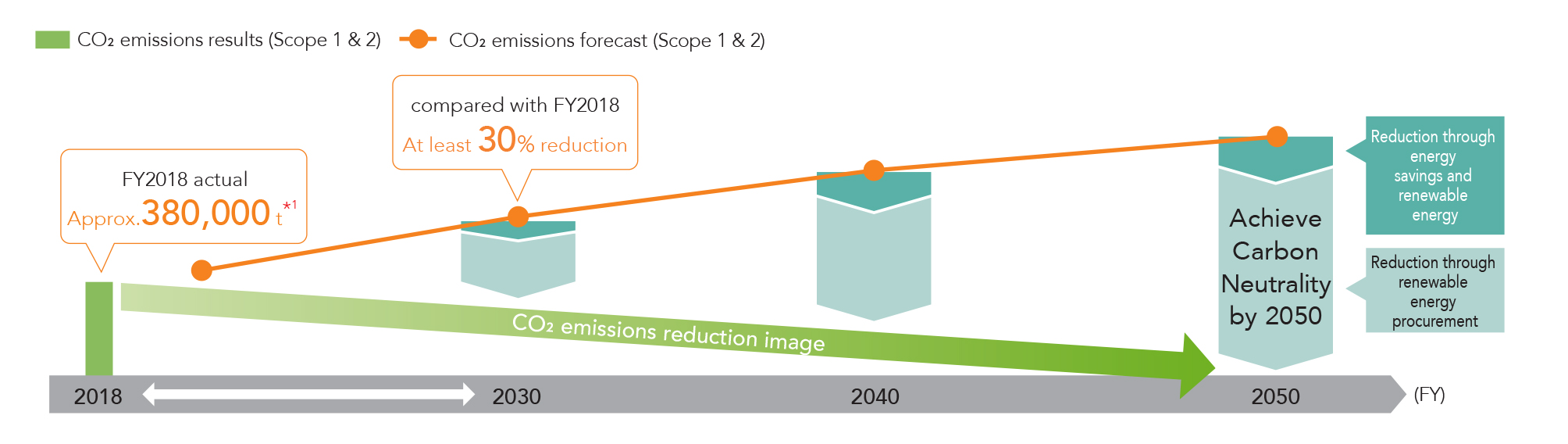
※ GS Yuasa Group's CO2 emissions aggregation standards have been changed, and in FY2018, we are undergoing third-party verification again.
- Recalculated using the 2018 emission coefficient obtained from the Ministry of the Environment and IEA
- Adopted the control standard as the calculation standard, and consolidated subsidiaries that can be directly influenced are included in the scope of calculation.
■Efforts Through Achieving Carbon Neutrality
|
|
|
■Contribute to reducing CO_{2} emission by environmentally considered products
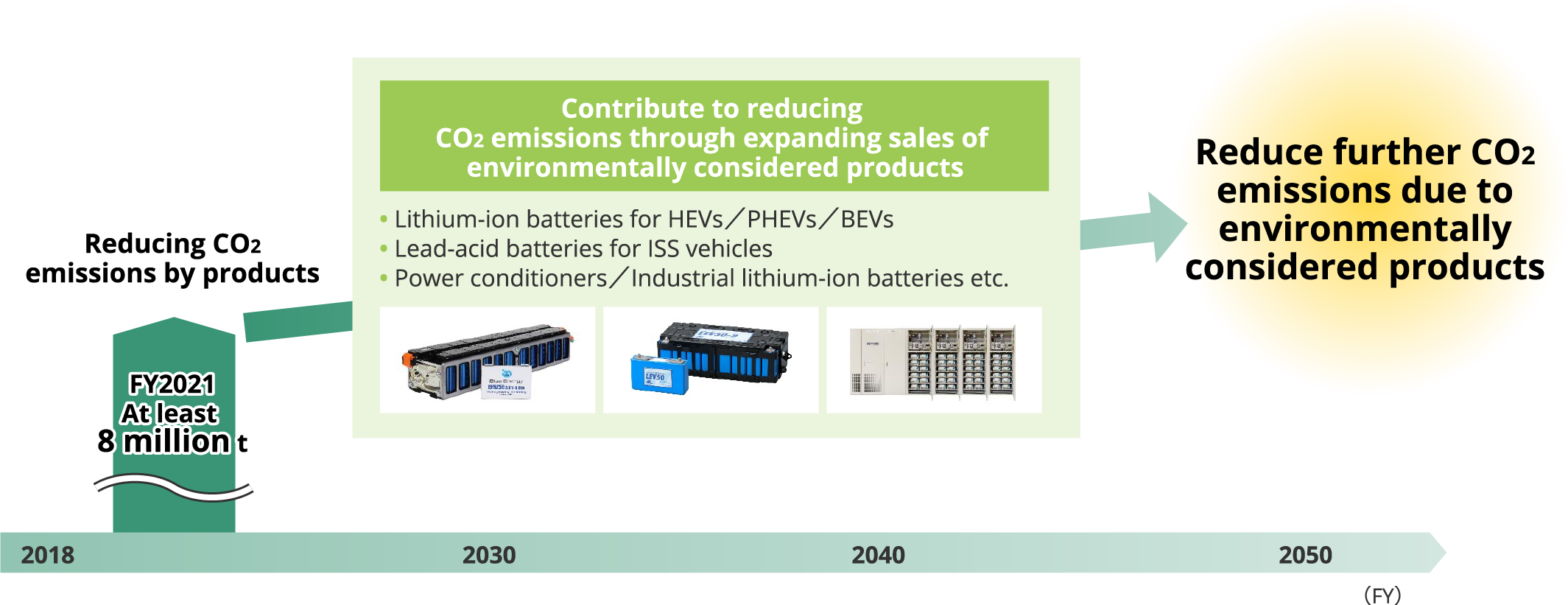
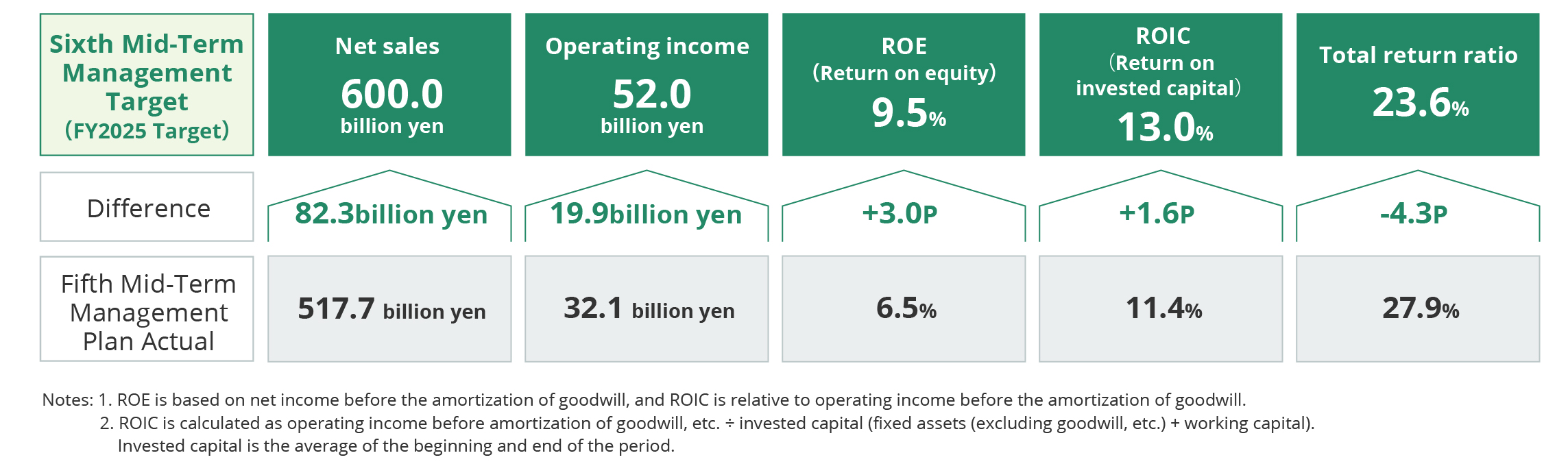
Positioning this period as one for laying the foundation for reform to realize the vision envisioned in Vision 2035,
we will implement a variety of measures to reform our business structure.
|
1.Development of batteries for BEVs |
|
|---|
|
2.Reinforcement of earning capacity in existing business |
|
|---|
|
3.DX / new business |
|
|---|
■Mid-Term Management Targets
■Segment Targets
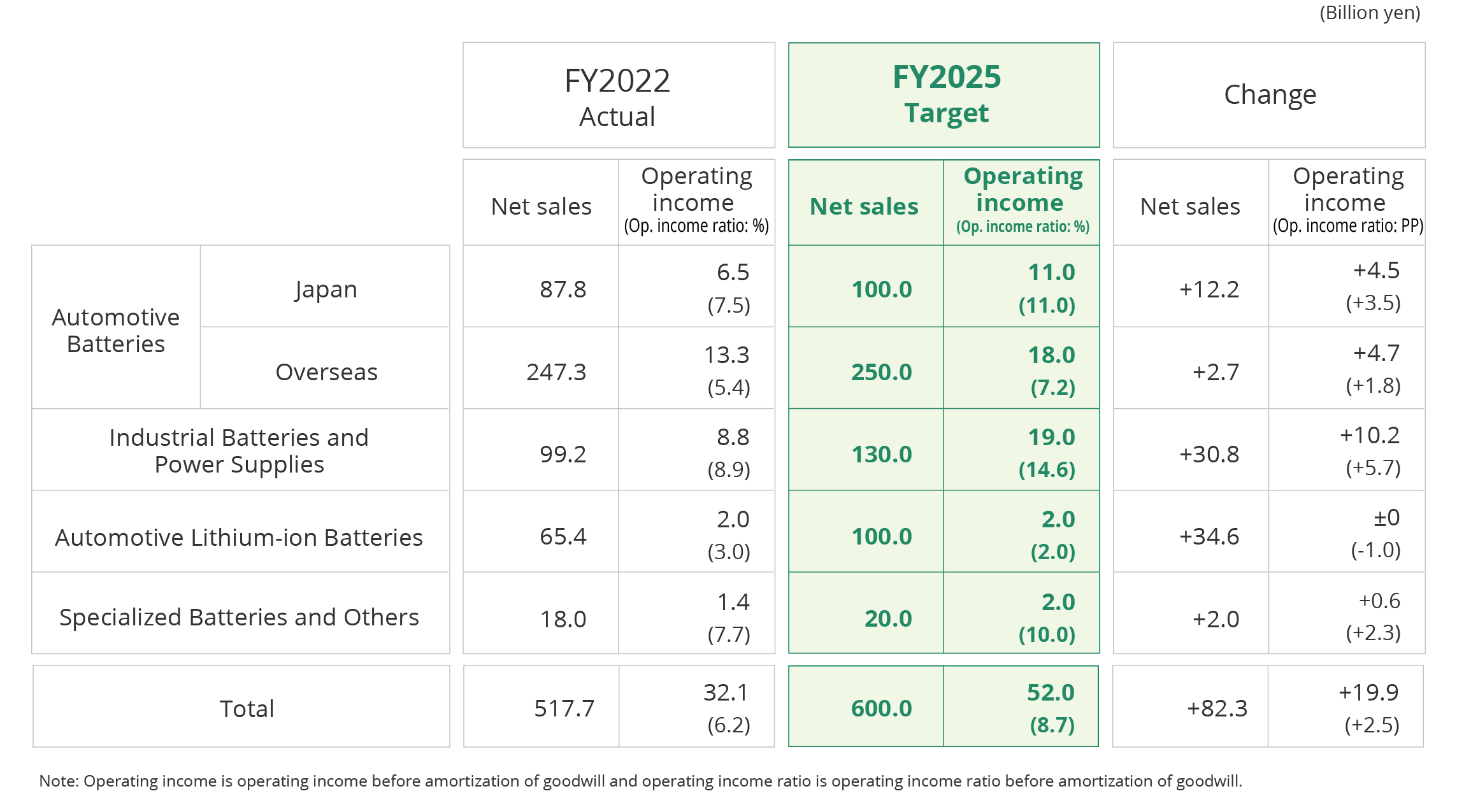
|
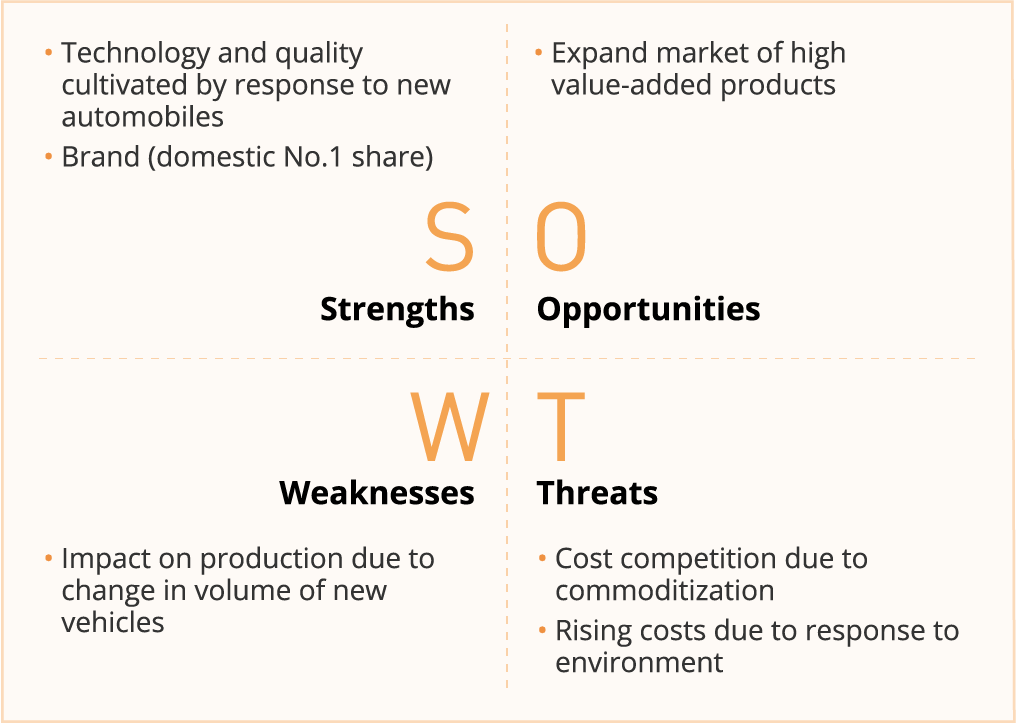
Automotive Batteries (Japan) |
■Business Policy
Build an optimal supply system in response to change of business environment and improve profit rate
■Strategies and Important Tasks
|
Establish supply system that enables both rapid response to demand fluctuations and inventory reduction |
|
|
Improve profit ratio due to optimal price revision such as raw material prices |
|
|
Rebuilt marketing strategies and maintain high market share Improve efficiency utilizing IoT and DX |
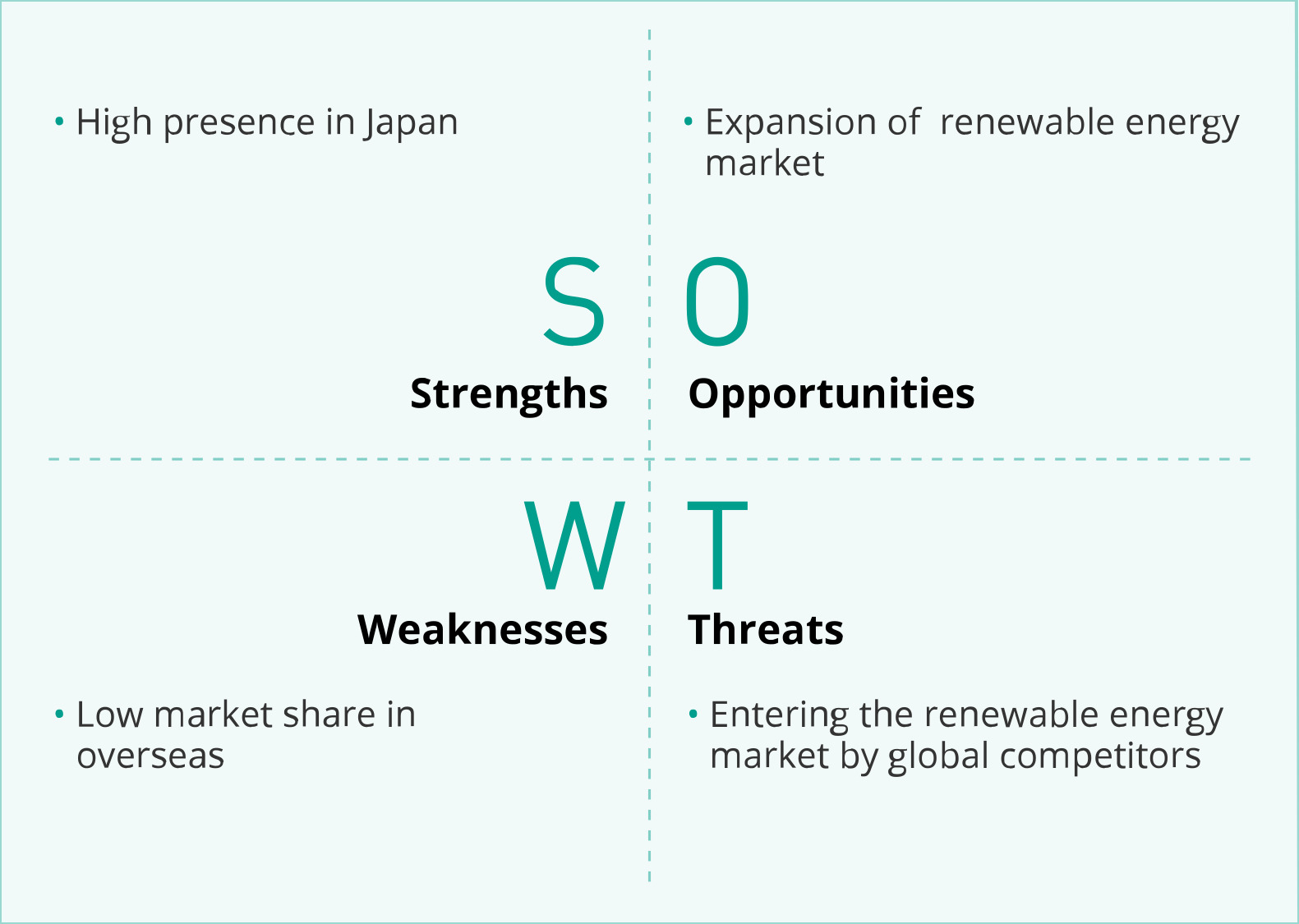
■SWOT
|
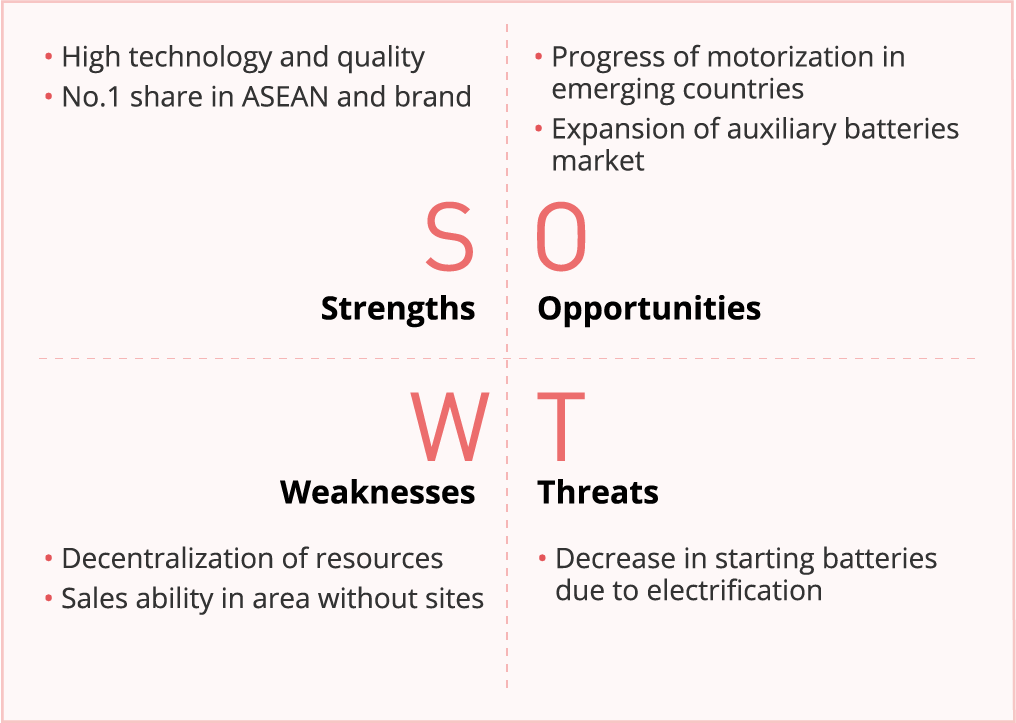
Automotive Batteries (Overseas) |
■Business Policy
Reform management structure for the future by selection and concentration and strengthen profitability
■Strategies and Important Tasks
|
Maximize profit by strengthening sales in ASEAN area |
|
|
Promote fundamental review of business |
|
|
Supply steadily to Europe utilizing Turkish site and expand sales to the Middle and Near East or North Africa |
|
|
Strengthen production base and expand market share of replacement batteries |
■SWOT
■Strategy by Region
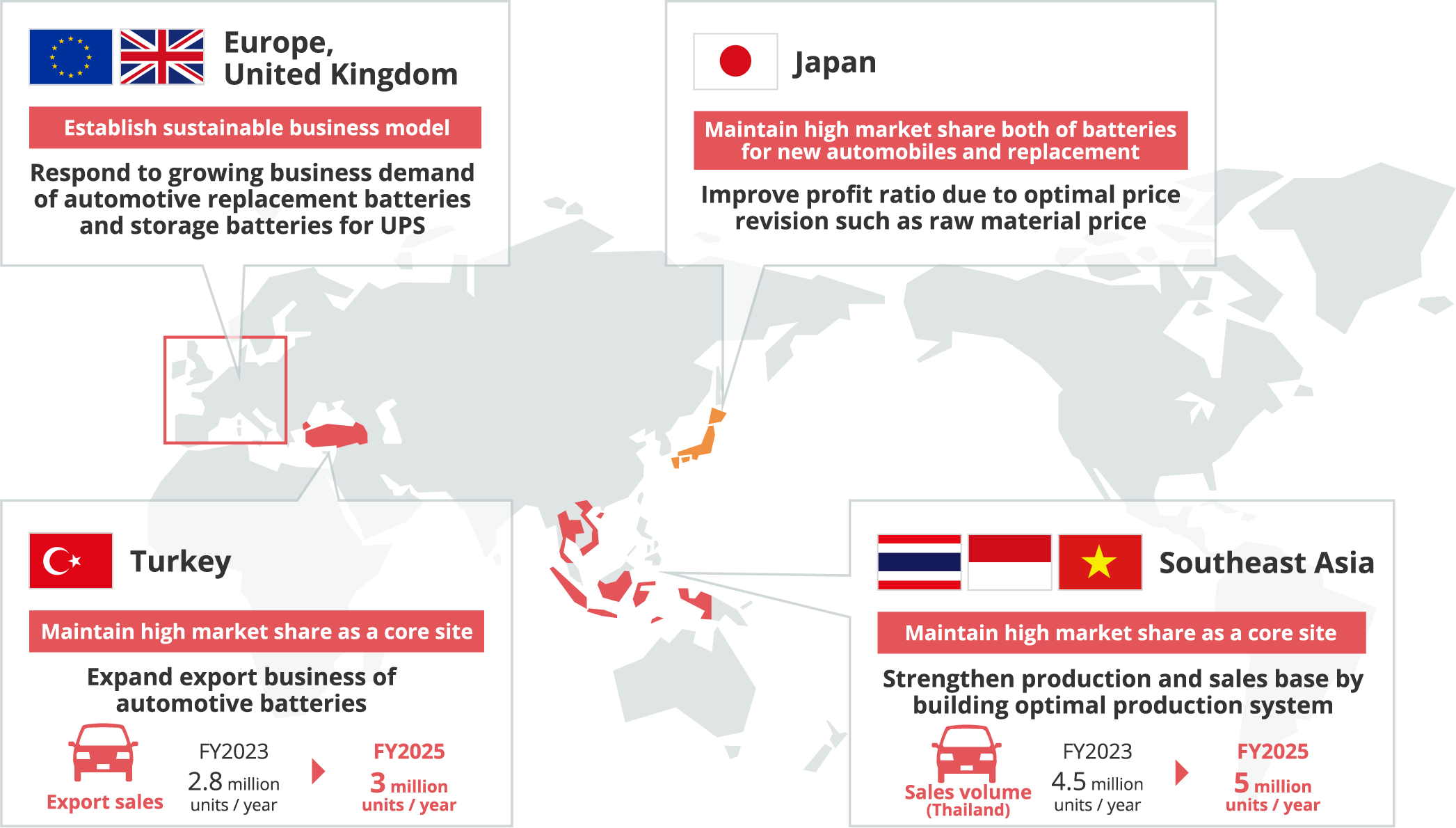
|
Industrial Batteries and Power Supplies |
■Business Policy
Building a business foundation to capture the growth of the next generation
■Strategies and Important Tasks
|
Expand our remote monitoring services Maximize profit by utilizing unparalleled superiority |
|
|
Setting the stage for a second pillar of business |
|
|
Strengthen competitive ability by expanding product lineup |
■SWOT
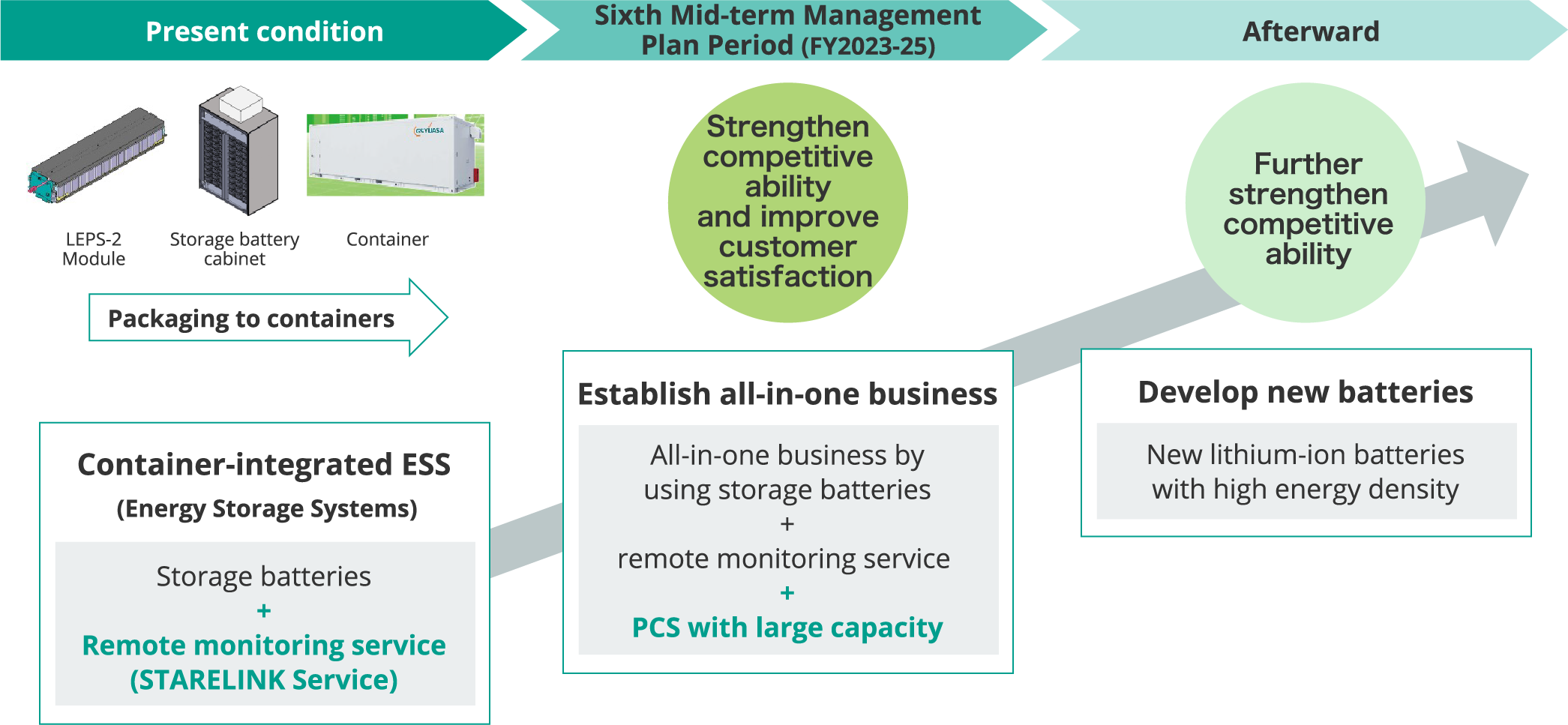
■Strategy of Regular Field
As the introduction of renewable energy expands, the importance of storage batteries for controlling fluctuations and adjusting supply and demand is expanding. We will enhance the value we provide to our customers and increase our presence in the regular field market through our all-in-one business, in which we offer power conditioners and storage batteries as a package and can provide everything from products to installation and maintenance in an integrated system.
|
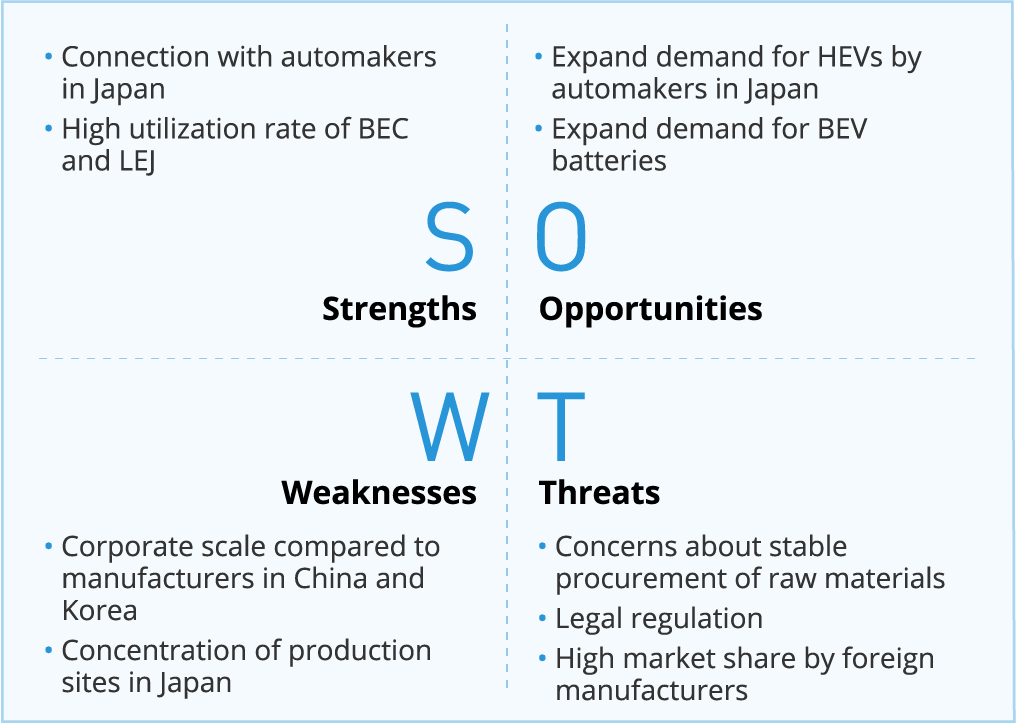
Automotive Lithium-ion Batteries |
■Business Policy
Achieve sustainable growth in the lithium-ion battery business by taking carbon neutrality and government targets as opportunities
■Strategies and Important Tasks
|
Improve yield rate and plant utilization rate Establish further increasing production system of Blue Energy No.2 plant Strengthen development and production systems of batteries for PHEVs |
|
|
Strengthen development systems of batteries for BEVs Prepare for entering market of batteries for BEVs |
|
|
Development of products / preparation of production |
■SWOT
■Strategy of batteries for BEVs
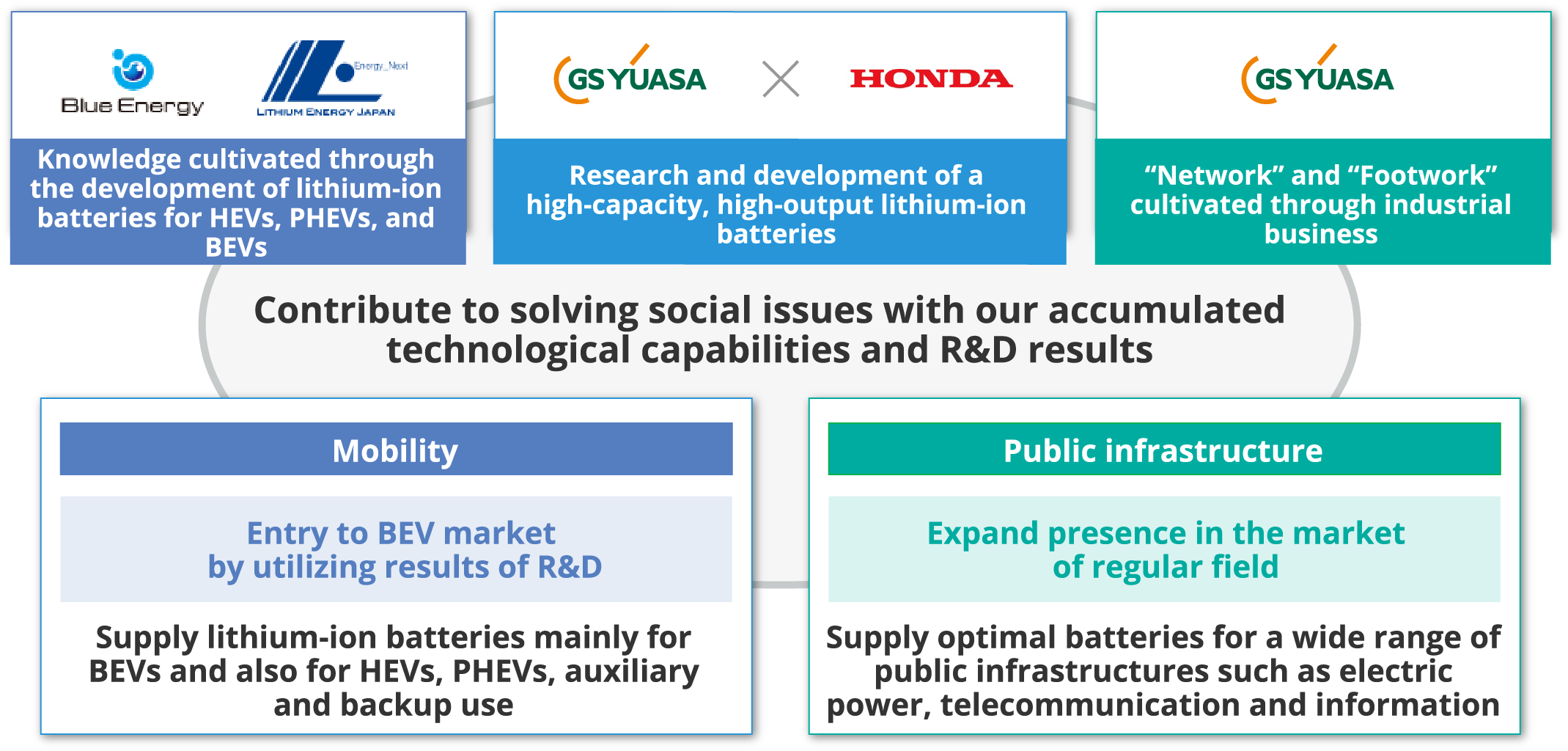
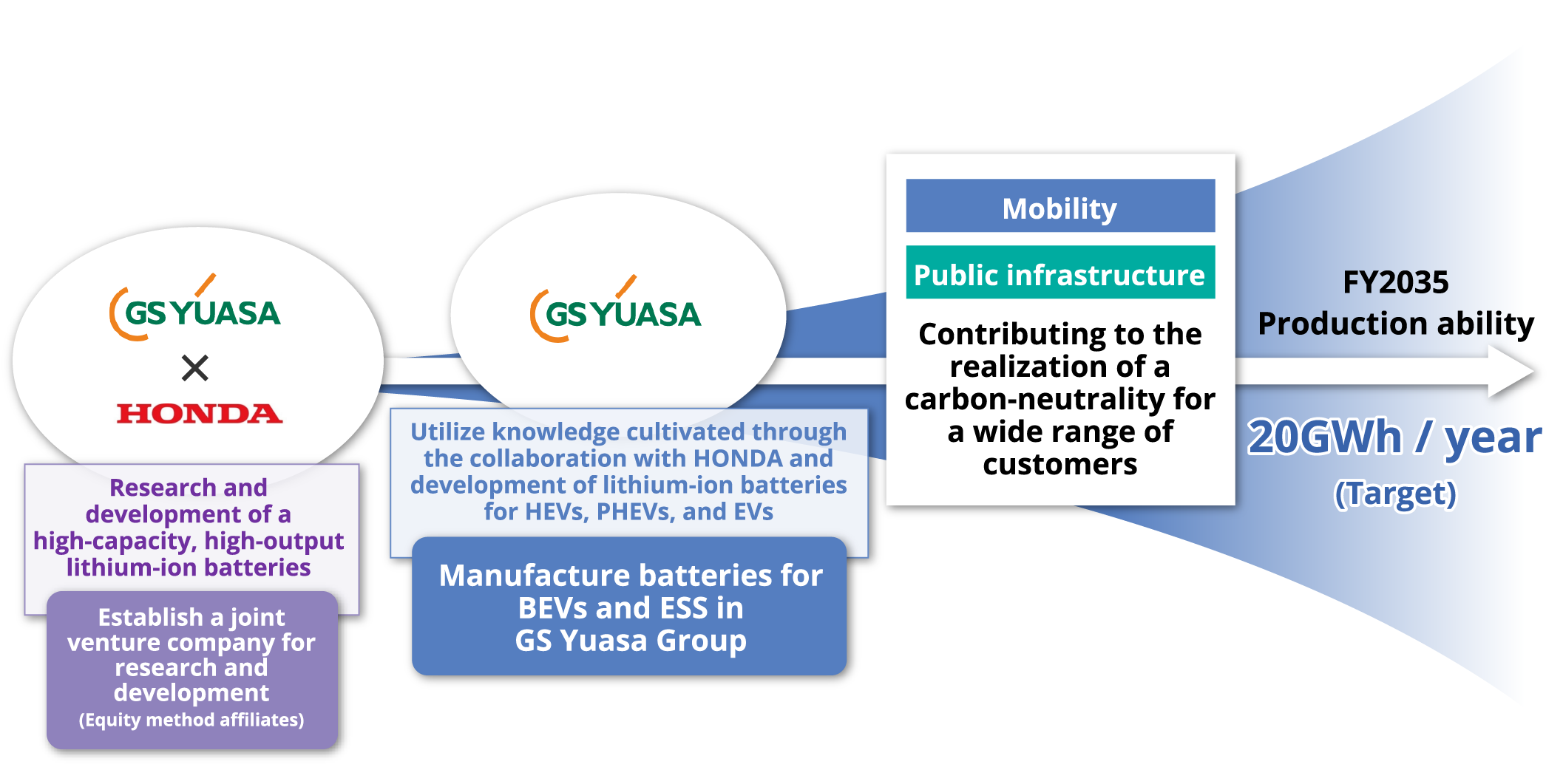
By using the results of research and development at Honda・GS Yuasa EV Battery R&D Co., Ltd., a new company established with Honda Motor, we plan to start operation of a production line in April 2027 and start full-scale mass production in October of that year for mass production of lithium-ion batteries for BEVs, the pillar of the mobility business. We will supply the batteries mainly to Japanese automakers, and by launching a series of production lines through 2030, the combined production capacity of GS Yuasa, Honda Motor, and Blue Energy will reach 20 GWh/year. We will later seek to expand production capacity within the GS Yuasa Group alone to more than 20 GWh/year by 2035.
■Strategy of batteries for HEVs
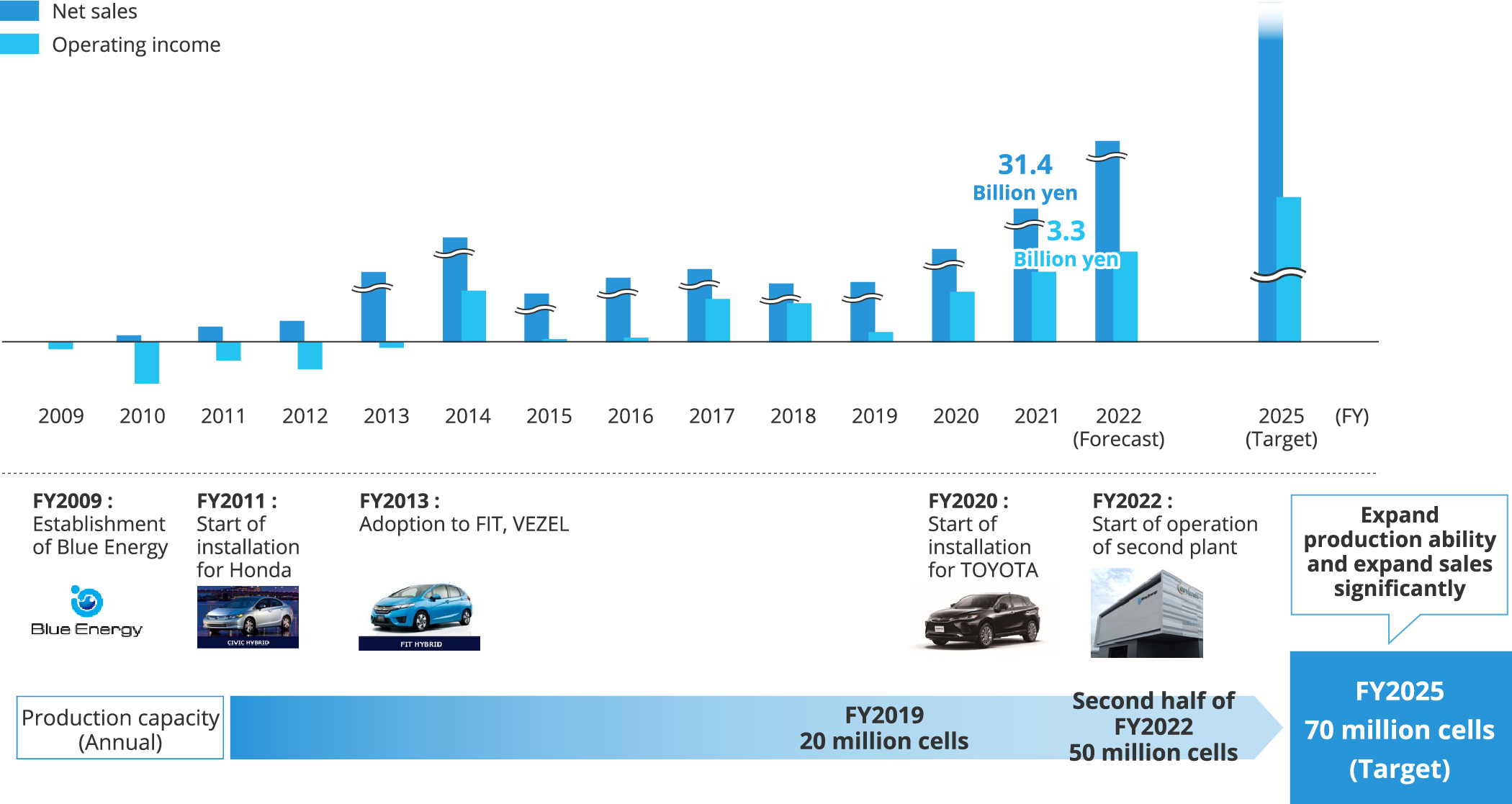
We expect that during the term of the Sixth Mid-Term Management Plan, sales volume of batteries for HEVs will increase, and we plan to increase Blue Energy’s production capacity to 70 million cells annually in fiscal 2025.
<Change in net sales and operating profit of Blue Energy>
|
Specialized Batteries and Others |
■Business Policy
Contribute to the building of new public infrastructure through batteries with the highest level of performance and quality
■Strategies and Important Tasks
|
Improve profitability due to efforts to strengthen the foundation of the defense industry Development of next-generation LiB for submarines Response to expand sales of LiB for aircrafts Expand sales of LiB for satellites |
|
|
Increase in environmental response costs Increase in costs for DX and creation of new business |
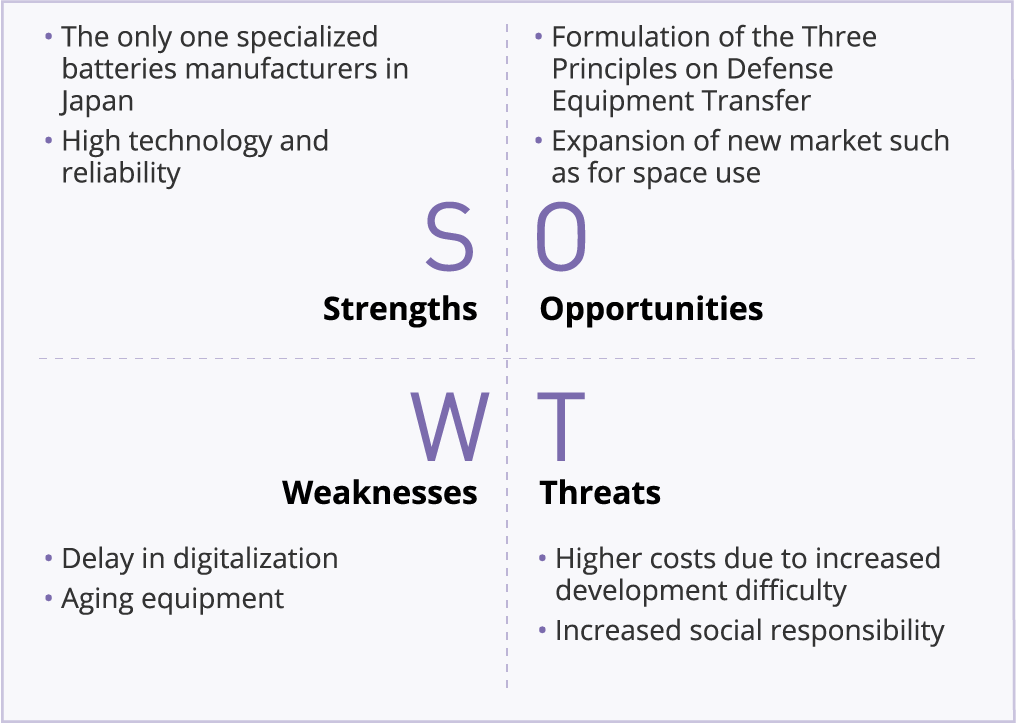
■SWOT
■Financial Policy
|
FY2025 Targets |
Interest-bearing debt to operating cash flow ratio*1 |
Total return ratio*2 |
Equity ratio |
- Interest-bearing debts (including lease obligations) / operating cash flow
- The total return ratio for FY2025 is before goodwill amortization
|
Sixth Mid-Term Management Plan 3-year total |
Operating cash flow |
Investing cash flow |
Free cash flow |
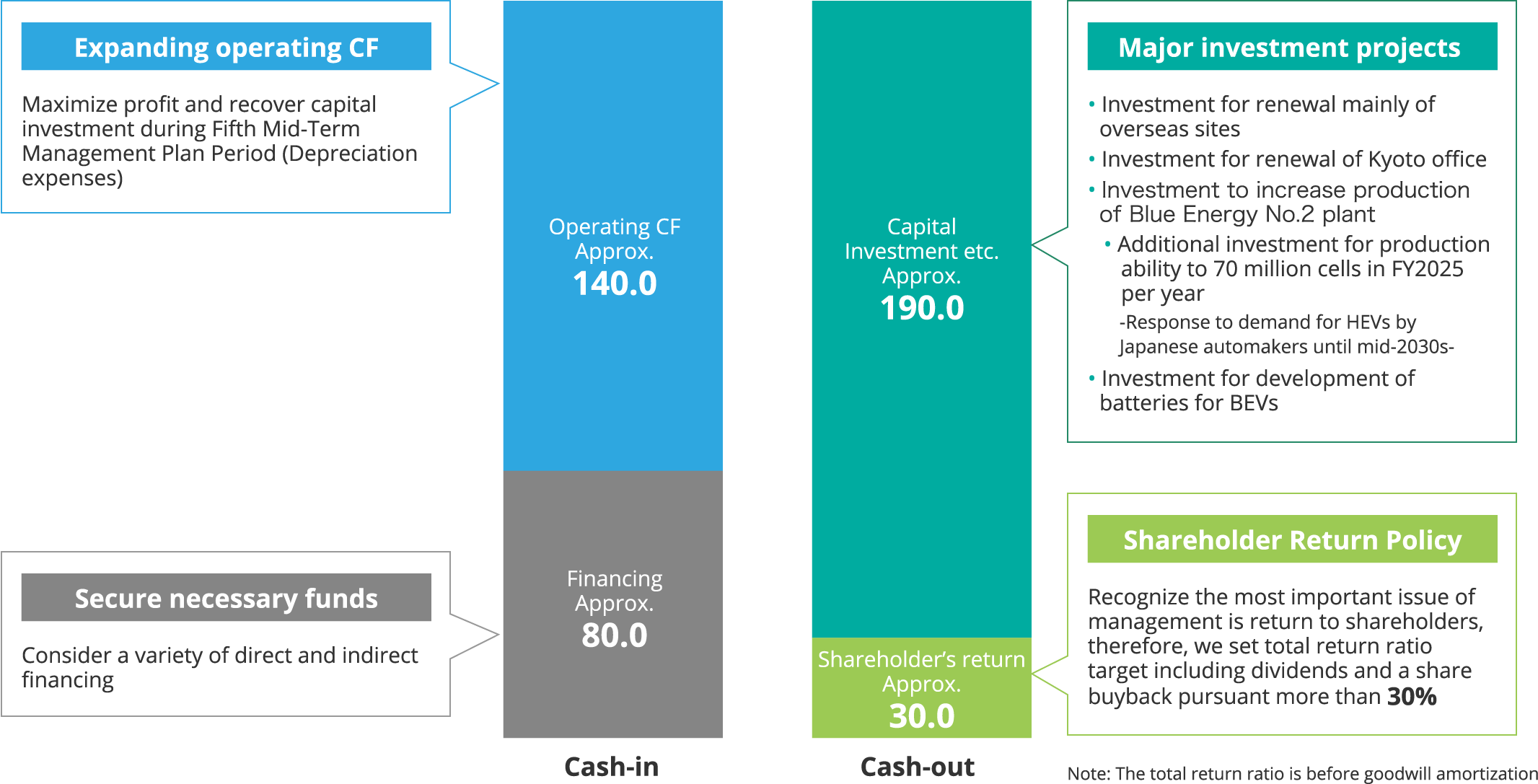
■Capital Allocation
May 21, 2019
May 13, 2016


